*This post is part of a much larger pillar blog: The Complete Guide to Controlled Environments
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Dry rooms are critical for various industries that require restricted humidity levels. The importance of dry rooms for pharmaceuticals, electronics, battery, automotive and aerospace industries cannot be overstated.
In this blog, our team will answer: What is a dry room?
We will explore the benefits and applications of dry rooms and how they can help increase drug stability, create an environment conducive for battery production and prevent corrosion in electronic components.
Make sure to check out our blog for more information on related topics. Without further ado, let’s get into it.
What is a Dry Room?
A dry room is a controlled environment that regulates the level of humidity and temperature.
The purpose of a low-humidity room is to protect sensitive equipment and products from moisture damage.
In order for a controlled environment to be classified as a low-humidity room, it typically needs to have below 40% relative humidity.
This is the threshold beyond which specialized humidity control systems are necessary.
Key components of this type of environmental room include your desiccant, ESD flooring (or other ESD applications), pre and post-cool cycles, and a traditional HVAC system.
Less stringent dry rooms will be in the ballpark of 10-30% relative humidity (rh), ultra-high performance dry rooms are characterized by their dew point.
Dew point is the temperature at which water in the air condenses.
GET THE LATEST INDUSTRY NEWS DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
Stay on the forefront of your industry with our weekly e-newsletter.
Once the room is below 40% relative humidity, all dry rooms will use a combination of a desiccant, HVAC cooling system.
Depending on the humidity spec, the size and price of the cleanroom will increase accordingly.
This type of environmental room are commonly found in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, aerospace and a variety of other instances.
In the pharmaceutical industry, humidity and temperature control can increase drug stability and shelf life by up to 50% .
In the electronics industry, humidity control is crucial to prevent static electricity discharge, which can damage sensitive components.
Aerospace and defense applications require extremely low levels of humidity to prevent corrosion and damage to electronic components.
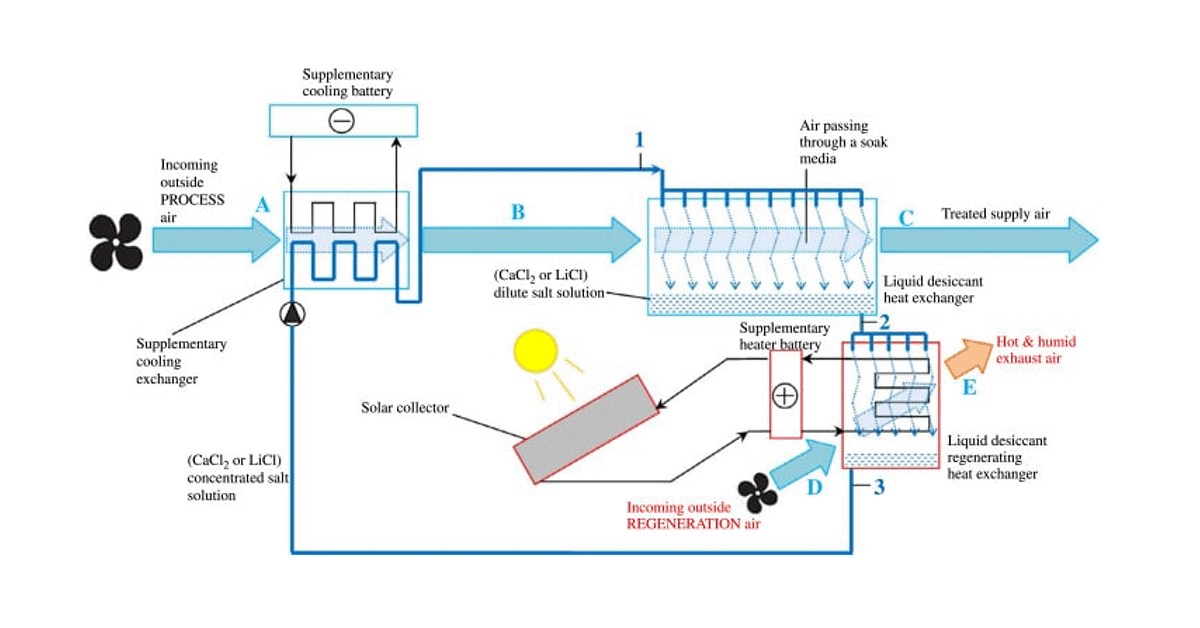
What Industries Commonly use a Low-Humidity Room?
Dry rooms are commonly used in industries that require precise humidity and temperature control, such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, aerospace, and food processing.
Why are Dry Rooms Important?
Dry rooms are important because they can protect sensitive materials, equipment, and products from moisture damage, contamination, and other environmental factors that could compromise their quality or safety.
How do Low-Humidity Rooms Maintain Humidity and Temperature Levels?
Common methods for maintaining humidity and temperature control in a dry room include HVAC systems, desiccant systems, stand-alone dehumidifiers, and humidity sensors.
What is Important to Consider when Designing a Dry Room?
When designing a dry room, it’s important to consider factors such as the desired humidity and temperature levels, the materials and equipment that will be used in the room, the size and layout of the room, and any regulatory requirements or standards that must be met.
Dry Room Industry Standard Compliance
To ensure compliance with industry standards in a dry room, it’s important to regularly monitor and maintain the humidity and temperature levels, use appropriate equipment and materials, follow standard operating procedures, and conduct regular inspections and audits.
What are Common Problems with Dry Rooms?
Common challenges associated with maintaining a dry room include equipment failure, changes in environmental conditions, contamination from external sources, and the cost and complexity of implementing and maintaining humidity and temperature control systems.
Desiccant Systems and Humidity
Having the proper desiccant system in place goes hand in hand with humidity control.
The desiccant system is the most expensive, but also the most important part of your room.
Properly sizing the desiccant system to your room size and humidity spec is crucial for maintaining an efficient and successful process.
When designing these systems, we take into consideration a wide variety of factors, such as the occupancy, in-room processes, vapor infiltration, and climate of the install location.

Humidity levels are measured using relative humidity sensors in real time.
It’s also important to keep in mind the relationship between humidity and temperature in a dry room.
This is all great information, but how much does a low-humidity room cost?
What are Low-Humidity Room Best Practices?
Best practices for operating a low-humidity room include regular maintenance and calibration of equipment, frequent monitoring and documentation of humidity and temperature levels, use of appropriate personal protective equipment, and proper training for personnel who work in the room.
GET THE LATEST INDUSTRY NEWS DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
Stay on the forefront of your industry with our weekly e-newsletter.
The Cost of Building and Operating a Dry Room
The costs associated with building and operating a low humidity room can vary depending on the size and humidity spec you’re aiming to have.
It’s difficult to estimate the cost of building a low-humidity room, especially facilities with dew points at -40° or lower, but you should expect upwards of $600 per sq/ft.
You also need to consider the cost of sealing the room to prevent infiltration.
Equipment, maintenance, and energy expenses are also significant costs to consider.
In the food and drug industry, FR-21-CFR Part 11 is a key regulation that controls the means of access between controlled environments, which can potentially increase the expected cost of the room due to how it complicates your low-humidity room’s electronic operating system.
Calibration standards and related material handling expenses are also essential considerations when building and operating a low-humidity room.
When calculating cost, you should take into account both the initial construction cost, and the cost to operate the room long term to ensure a good ROI.
It’s also important to mention that your existing facility’s utilities, such as the existence of steam and chilled water, can help mitigate the cost of your overall system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dry rooms are critical for various industries that require specific humidity and temperature levels.
They can help increase drug stability, prevent static electricity discharge, and prevent corrosion in electronic and metal components.
HVAC systems can account for up to 40% of a building’s energy use, making efficient humidity and temperature control essential for cost savings.
The desiccant industry is expected to reach $3.9 billion by 2026, highlighting the importance of moisture control methods.
Low-humidity rooms are a reliable and consistent method of moisture control that can help protect sensitive equipment and products.
If you want to learn more, or are interested in building a dry room, contact us.