*This post is a pillar post for mechanical systems. Make sure to periodically check back for more blogs on this topic linked throughout this article.
Table of Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems are integral to maintaining indoor air quality and comfort in commercial buildings.
HVAC systems are designed to regulate temperature, humidity, and air flow, ensuring a healthy and productive environment for occupants.
In commercial settings, HVAC systems play a crucial role in maintaining operational efficiency and compliance with health and safety standards.
A well-functioning HVAC system ensures that employees, customers, and visitors are comfortable, which can enhance productivity, customer satisfaction, and overall well-being.
The Purpose of this Guide
This guide aims to provide building owners, facility managers, and other stakeholders with comprehensive information about HVAC systems in commercial buildings.
It covers the various types of systems, their components, installation and maintenance practices, energy efficiency considerations, and emerging trends.
By understanding these aspects, decision-makers can make informed choices to optimize the performance and sustainability of their HVAC systems, ensuring long-term operational efficiency and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Click here for an extremely in-depth article completely going over just how Commercial HVAC Systems work.
Understanding HVAC Systems
To start off this article, we’re going to take a wide look at HVAC systems as a whole, and discuss basic components of any HVAC system and how they work.
Basic Components of HVAC Systems
In any HVAC system, the basic components you’ll see include heating units, ventilation units, and air conditioning units. What specific equipment makes up these units, though?
Heating Units
Boilers:
Use water or steam to generate heat, often fueled by natural gas, oil, or electricity.
Boilers are common in larger buildings and provide consistent and efficient heating.
Furnaces:
Heat air directly using natural gas, oil, or electricity, and distribute it through ductwork.
Furnaces are typically used in smaller to medium-sized buildings and can quickly respond to temperature changes.
Ventilation Systems
Natural Ventilation:
Natural ventilation relies on windows, doors, and passive means to allow air flow.
It is energy-efficient but depends heavily on weather conditions and building design.
Mechanical Ventilation:
Mechanical Ventilation uses fans and ductwork to control air flow and ensure adequate ventilation. Mechanical systems can operate independently of outdoor conditions and are essential in tightly sealed buildings to maintain indoor air quality.
GET THE LATEST INDUSTRY NEWS DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
Stay on the forefront of your industry with our weekly e-newsletter.
Air Conditioning Units
Central Air Conditioners:
Central air cools air at a central location and distributes it through ductwork. Central systems are ideal for maintaining consistent temperatures across large spaces.
Split Systems:
Split systems consist of an outdoor unit (condenser) and an indoor unit (evaporator), providing localized cooling. Split systems offer flexibility and can be installed in various configurations to meet specific cooling needs.
How HVAC Systems Work
When you combine any of the above components, you’re left with an HVAC system. Here’s how each of the different processes work.
The Heating Process
The heating process involves generating heat through a furnace or boiler and distributing it via ductwork or radiators to maintain desired indoor temperatures.
Furnaces typically heat air directly, while boilers heat water or produce steam, which is then circulated through radiators or underfloor heating systems.
The Cooling Process
Air conditioning units remove heat from indoor air using refrigerants. The refrigerant absorbs heat from the indoor air at the evaporator coil, then expels it outdoors at the condenser coil. This process reduces the indoor air temperature and controls humidity levels.
Air Circulation and Filtration
Fans and ductwork circulate air throughout the building, ensuring consistent temperature and air quality. Filters within the system remove particulates, allergens, and pollutants, enhancing indoor air quality and protecting the HVAC components from dust and debris.
Types of HVAC Systems for Commercial Buildings
Now that we have a general understanding of these systems, let’s look at the different options you’ll have for your commercial building.
Single Split Systems
First up, single split systems.
Description and Components
A single split system consists of an outdoor unit connected to an indoor unit. The system provides cooling to individual rooms or small spaces, and if configured as a heat pump, heating as well.
Key components include a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and refrigerant lines.
The Pros and Cons
Pros:
Affordable, easy to install, and allows individual room control, making it suitable for small offices or retail spaces.
Cons:
Multiple units are required for larger buildings, which can be costly and occupy significant space.
Multi-Split Systems
Now, let’s talk about multi-split systems.
Description and Components
A multi-split system is similar to a single split system but connects one outdoor unit to multiple indoor units. This setup provides more extensive coverage and can serve multiple rooms or zones.
The Pros and Cons
Pros:
Efficient use of space, better control over multiple zones, and fewer outdoor units needed, reducing the visual and physical impact on the building exterior.
Cons:
Higher initial cost and more complex installation and maintenance requirements.

VRF (Variable Refrigerant Flow) Systems
Time for a bit of a complex one, VRF systems.
Description and Components
VRF systems use multiple indoor units connected to a single outdoor unit, with the ability to vary refrigerant flow based on demand. This allows for precise temperature control in different zones.
The Pros and Cons
Pros:
Highly energy-efficient, flexible installation, and precise temperature control for various zones, making it ideal for larger buildings with diverse needs.
Cons:
High initial cost and requires skilled technicians for installation and maintenance.
Heat Pump Systems
Next up, heat pump systems.
Description and Components
Heat pump systems transfer heat between the building and the outside air (air-source) or ground (ground-source) to provide heating and cooling. Components include an outdoor unit, indoor air handler, and refrigerant lines.
The Pros and Cons
Pros:
Energy-efficient, reduces carbon footprint, and can provide both heating and cooling, making them versatile for different climates.
Cons:
Performance can drop in extreme temperatures, and higher initial installation costs compared to conventional systems.
Rooftop Units (RTUs)
Finally, rooftop units (RTUs).
Description and Components
Rooftop units are packaged systems placed on rooftops, combining heating and cooling elements in one unit. They are commonly used in large commercial spaces like shopping malls and warehouses.
The Pros and Cons
Pros:
Saves indoor space, easy maintenance access, and suitable for large spaces, providing efficient temperature control.
Cons:
Exposed to weather elements, which can affect durability and performance, and installation can be complex due to the need for roof support.
Designing HVAC Systems for Commercial Buildings
So, how are these HVAC systems designed? As a design-build contractor, our team specializes in fitting the right commercial HVAC system into your building. In this section, we’ll touch a little bit on our process for designing these systems.
Assessing Building Needs
The first step in this process is assessing the needs of the building. Each situation is different, and needs a strong initial assessment to determine HVAC system needs.
Size and Layout
Consider the total square footage, number of floors, and specific layout to determine the appropriate HVAC system size and configuration.
An accurate load calculation ensures the system can handle the building’s heating and cooling demands without excessive energy consumption.
Occupancy Levels
Analyze the number of occupants and their activity levels to ensure the system can maintain comfort and air quality under varying loads.
High occupancy areas, like conference rooms or auditoriums, require robust ventilation and cooling solutions.
Specific Functional Requirements
Account for special areas like server rooms, kitchens, or manufacturing spaces that may have unique heating, cooling, or ventilation needs.
These areas often require tailored solutions to manage heat generation, humidity, and air quality.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
The second thing we look at in the design process is optimizing for energy efficiency.
Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient HVAC systems reduce operational costs, minimize environmental impact, and often qualify for rebates and incentives.
Efficient systems also contribute to sustainability goals and enhance building value.
GET THE LATEST INDUSTRY NEWS DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
Stay on the forefront of your industry with our weekly e-newsletter.
High-Efficiency HVAC Components
Invest in high-efficiency components such as variable speed fans, energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), and high-SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) air conditioning units.
These components can significantly reduce energy consumption and improve overall system performance.
Compliance with Regulations and Standards
Finally, we verify that all the work we’ve done is complaint with the regulations and standards local to where our client’s building is located.
Local Building Codes
Ensure the HVAC system design adheres to local building codes and regulations regarding energy use, safety, and environmental impact.
Compliance is essential to avoid penalties and ensure occupant safety.
Industry Standards (ASHRAE, LEED)
Follow industry standards set by organizations like ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air-Conditioning Engineers) and LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) to optimize system performance and sustainability.
These standards provide guidelines for energy efficiency, indoor air quality, and environmental impact.
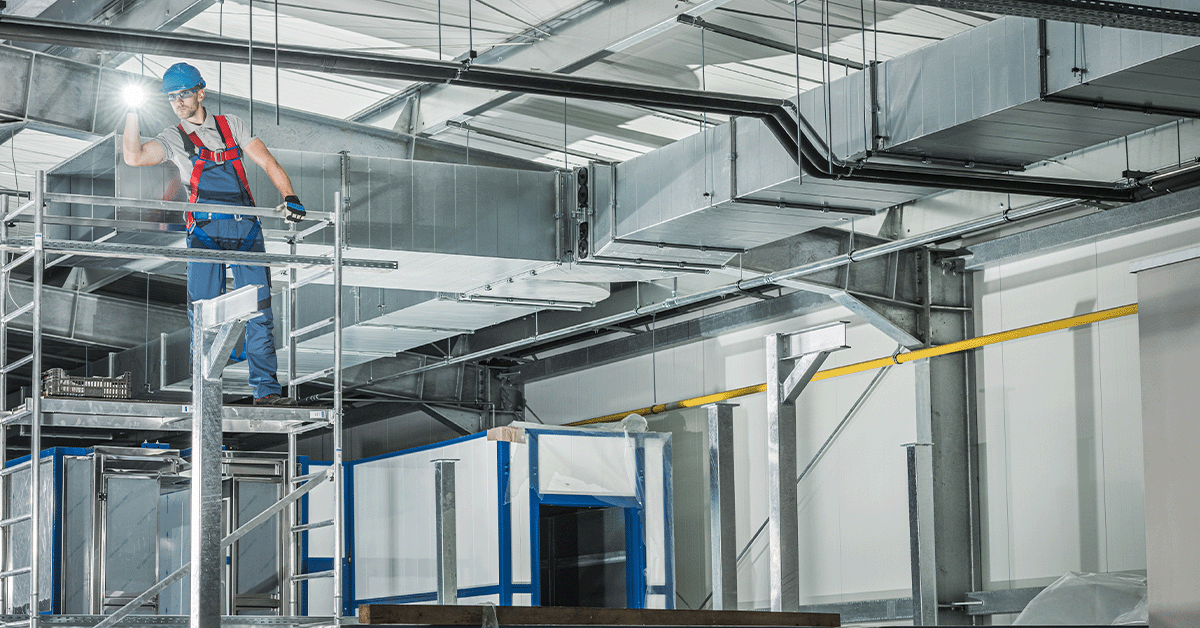
Installation of HVAC Systems
After the HVAC system is designed and manufactured to spec, it’s time for installation. Let’s take an inside look into how our field team does it.
Planning the Installation
Before any HVAC equipment is moved on site, our team will plan the installation ahead of time. This consists of site prep, and scheduling with other trades and the client.
Site Preparation
Prepare the building site by ensuring access for equipment, clear installation paths, and proper utility connections.
Site preparation may include reinforcing structural supports for heavy equipment and ensuring adequate space for installation and maintenance.
Scheduling and Coordination
Coordinate with other construction activities to ensure timely and efficient installation, avoiding delays and disruptions.
Effective scheduling minimizes downtime and ensures seamless integration with other building systems.
Hiring Professional Contractors
Now, if you’re working with AVM Group for your commercial HVAC project, this isn’t a step you’ll have to worry about. However, if you choose to go with another vendor, these are a few things you should keep in mind.
Selecting Qualified HVAC Contractors
Choose contractors with relevant experience, certifications, and a proven track record in commercial HVAC installations.
Verify credentials and check references to ensure the contractor has the necessary expertise and reliability.
Importance of Professional Installation
Proper installation is crucial for system performance, longevity, and warranty compliance.
Avoid DIY approaches for complex HVAC systems, as improper installation can lead to inefficiencies, increased energy costs, and premature equipment failure.
You absolutely need to work with a mechanical systems expert. Otherwise you will waste extremely valuable time and resources.
Key Installation Steps
When we actually go to install the system, these are the key steps that we follow.

Installing Heating and Cooling Units
Position and secure heating and cooling units according to the design specifications, ensuring proper clearance and ventilation.
Accurate placement is essential for optimal performance and ease of maintenance.
Ductwork and Ventilation Installation
Install ductwork and ventilation systems to ensure efficient air distribution and meet design requirements for airflow and air quality.
Proper sealing and insulation of ductwork prevent air leaks and energy loss.
System Testing and Balancing
Test the entire HVAC system to ensure it operates correctly, adjust settings for optimal performance, and balance airflow throughout the building.
System balancing involves adjusting dampers and vents to ensure even distribution of conditioned air.
GET THE LATEST INDUSTRY NEWS DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
Stay on the forefront of your industry with our weekly e-newsletter.
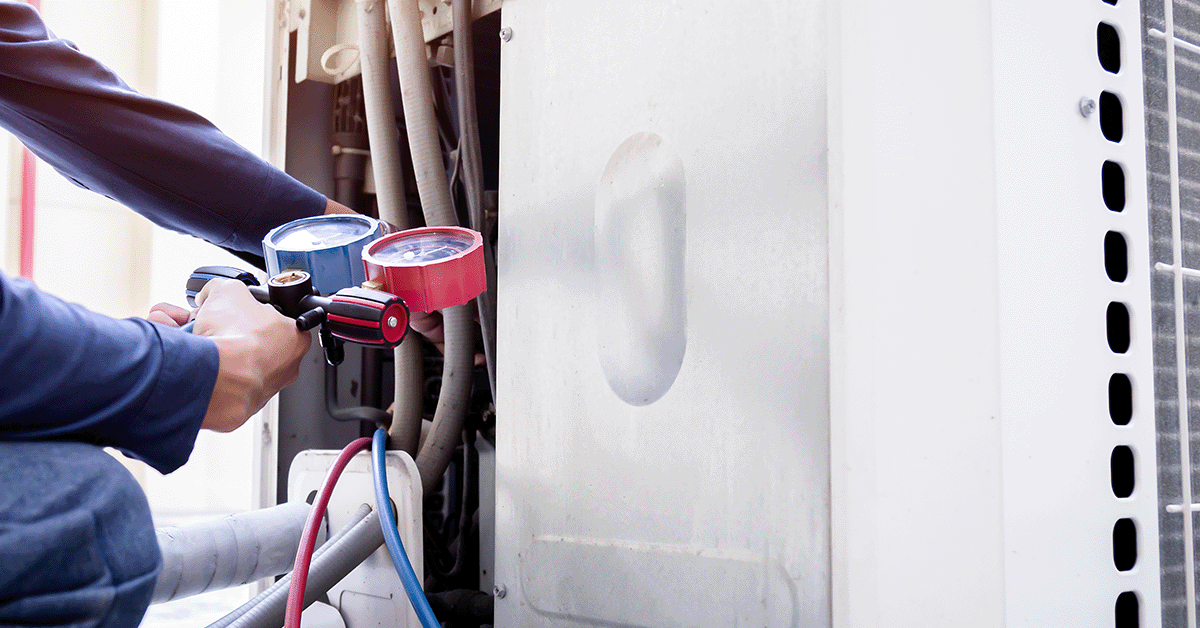
Maintenance and Management of HVAC Systems
Following the installation of your system, you’ll want to make sure that you are continually performing maintenance in order to prolong the life of your components, and eliminate any unnecessary downtime.
Regular Maintenance Tasks
We also do not recommend doing the maintenance yourself. Oftentimes, the same company who installed your system will also service it.
Filter Changes
Replace filters regularly to maintain air quality and system efficiency, typically every 1-3 months depending on usage and environment.
Dirty filters restrict airflow, reducing system efficiency and potentially causing damage.
Inspection and Cleaning of Components
Regularly inspect and clean components such as coils, fans, and ductwork to prevent buildup of dust, dirt, and debris that can impair system performance.
Clean components improve energy efficiency and extend the lifespan of the system.
Seasonal Tune-Ups
Schedule professional tune-ups in the spring and fall to prepare the system for peak heating and cooling seasons, ensuring all components are functioning optimally.
Tune-ups typically include inspecting the system, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring all components are in good working condition.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When doing maintenance, here are some common issues your service technician may run into.
Inconsistent Temperature Control
Check for issues like thermostat malfunctions, airflow obstructions, or refrigerant leaks that can cause uneven temperatures.
Ensure that thermostats are correctly calibrated and placed in optimal locations.
Poor Air Quality
Identify and address sources of indoor pollutants, improve ventilation, and ensure regular maintenance of air filters and cleaning of ductwork.
Consider using air purifiers or upgrading to higher efficiency filters if necessary.
Unusual Noises and Odors
Investigate and resolve sources of unusual noises and odors, which may indicate mechanical issues, blockages, or component failures.
Regular inspections can help identify and address these issues before they become serious problems.
Upgrading and Retrofitting HVAC Systems
Sadly, sometimes systems do break down, or become inefficient to the point of needing to be replaced.
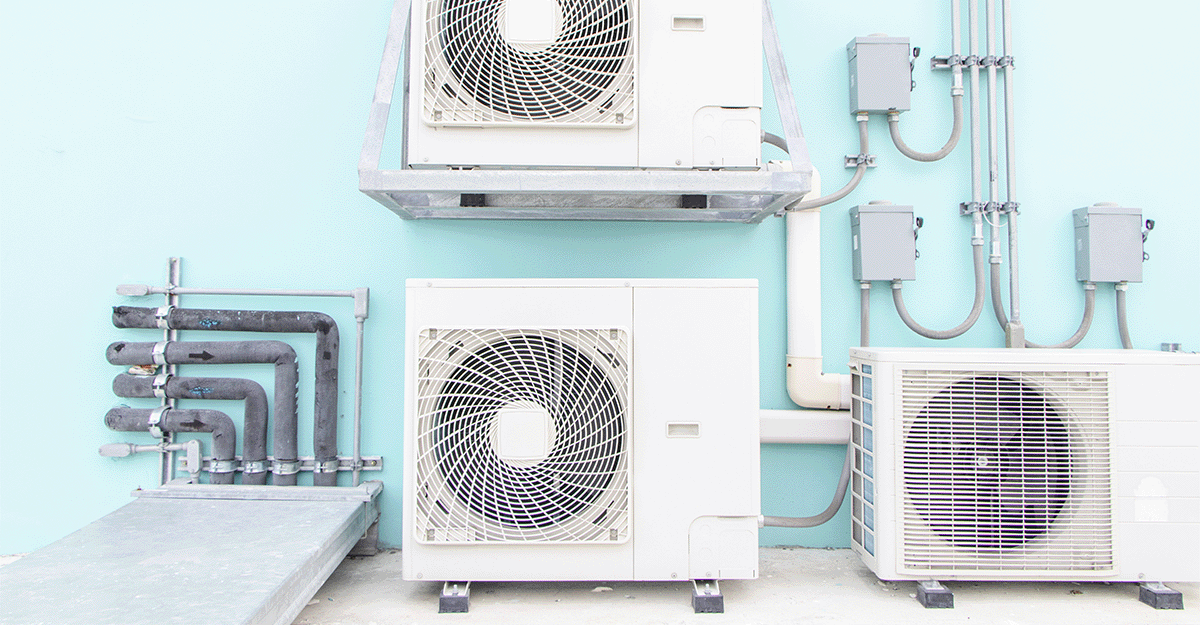
Identifying the Need for Upgrades
Monitor system performance, energy consumption, and maintenance costs to determine when upgrades or retrofits are necessary.
Older systems or those frequently requiring repairs may benefit from modern, energy-efficient replacements.
Modernization Options and Benefits
Consider modernizing with high-efficiency units, smart thermostats, or advanced controls to enhance system performance, reduce energy costs, and improve comfort.
Upgrades can also extend the lifespan of the system and enhance building value.
If you want a lot more information on this topic, check out our article: Upgrading and Retrofitting HVAC Systems.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in HVAC Systems
As with any industry, the need for energy efficiency and “green” solutions is extremely present in HVAC systems.
Implementing Energy-Efficient Practices
Here are some of the most common energy-efficient practices that your installation team should implement.
Programmable Thermostats
Use programmable thermostats to optimize temperature settings based on occupancy patterns, reducing energy waste during unoccupied periods. Smart thermostats can also provide remote access and advanced scheduling options.
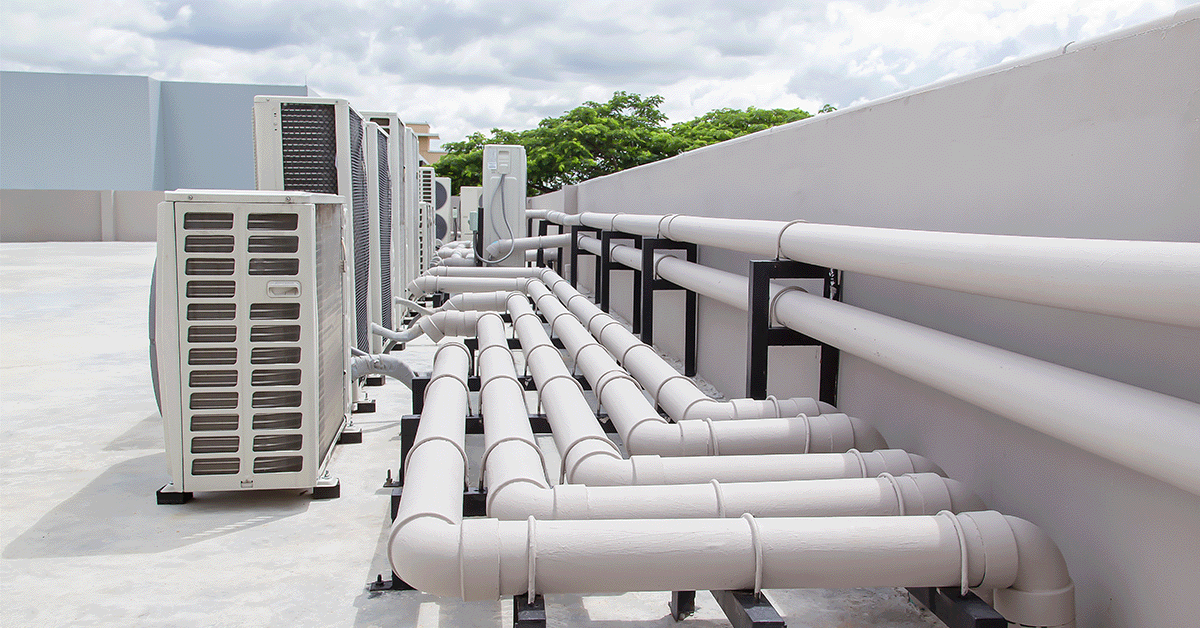
Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERVs)
Install ERVs to capture and reuse energy from exhaust air, improving ventilation efficiency and reducing heating and cooling loads. ERVs are particularly effective in buildings with high ventilation needs.
Sustainable HVAC Solutions
What are some actual components that promote sustainability in your system?
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Leverage the stable temperatures of the earth to provide efficient heating and cooling, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Geothermal systems have higher upfront costs but offer significant long-term energy savings and environmental benefits.
Solar-Powered HVAC Systems
Incorporate solar panels to power HVAC systems, reducing energy costs and environmental impact. Solar power can offset electricity usage and provide a renewable energy source for heating and cooling.
Benefits of Energy-Efficient and Sustainable Systems
What benefits can you expect to see from installing these systems?
Cost Savings
Reduce operational costs through lower energy consumption and potential eligibility for rebates and incentives. Energy-efficient systems can significantly lower utility bills and reduce long-term expenses.
Environmental Impact
Minimize carbon footprint and contribute to sustainability goals by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving energy resources. Sustainable HVAC solutions help mitigate climate change and promote a healthier environment.
Future Trends in Commercial HVAC Systems
Now that we’ve covered a myriad of topics related to the design, install, and maintenance of your new HVAC system, we think it’s important to talk about what you should expect from the HVAC industry in the coming years.
Advancements in HVAC Technology
Here are the most likely innovations we see on the horizon.
Smart HVAC Systems
Smart HVAC systems represent a significant leap forward in the automation and efficiency of climate control in commercial buildings.
These systems utilize advanced sensors, machine learning algorithms, and real-time data to optimize performance.
Smart thermostats can learn occupancy patterns and adjust settings accordingly, reducing energy consumption during off-peak hours while maintaining comfort.
These systems can be controlled remotely via smartphones or computers, allowing facility managers to monitor and adjust the settings from anywhere.
Predictive maintenance is another key feature, where the system can anticipate when components will fail and schedule maintenance before issues arise, thus preventing costly downtime and repairs.

Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming HVAC systems by connecting various components through the internet, enabling seamless communication and coordination.
IoT-enabled HVAC systems can collect and analyze data from different sensors, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality sensors, to optimize the environment automatically.
This integration allows for advanced features like energy monitoring, where the system tracks energy usage in real-time and suggests adjustments to improve efficiency.
Moreover, IoT devices can facilitate better air quality management by continuously monitoring pollutant levels and adjusting ventilation rates accordingly.
The result is a more responsive, efficient, and environmentally friendly HVAC system.
Emerging Standards and Regulations
In addition to new tech, changes in standards and regulations should also be kept in mind.
Impact of New Legislation
Legislation and regulations are becoming increasingly stringent, driving advancements in HVAC technology and practices.
Governments worldwide are implementing policies aimed at reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
For instance, the introduction of new building codes requires higher energy efficiency standards for HVAC systems.
Regulations may also mandate the use of low-global-warming-potential (GWP) refrigerants to mitigate climate change.
These legislative changes compel manufacturers and building owners to adopt more sustainable practices and invest in advanced HVAC technologies that comply with new standards.
Trends in Energy Efficiency Standards
Energy efficiency standards for HVAC systems are continually evolving to encourage the adoption of more efficient technologies.
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) are benchmarks for cooling efficiency, while the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) measures heating efficiency.
Higher SEER, EER, and HSPF ratings indicate more efficient systems. In recent years, the trend has been toward higher minimum efficiency requirements, pushing manufacturers to innovate and develop systems that consume less energy while delivering optimal performance.
Additionally, building certification programs like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) are setting high standards for energy efficiency and sustainability, encouraging the integration of renewable energy sources and advanced control systems in HVAC design.
Conclusion
HVAC systems are essential for maintaining comfortable, healthy, and productive environments in commercial buildings.
This guide has explored the fundamental components of HVAC systems, including heating units, ventilation systems, and air conditioning units, as well as their working principles.
We delved into the various types of HVAC systems suitable for commercial applications, such as single split systems, multi-split systems, VRF systems, heat pumps, and rooftop units.
The importance of proper design, installation, and maintenance was emphasized, highlighting the need for energy efficiency and compliance with regulations.
Proactive management of HVAC systems is crucial for ensuring long-term performance and sustainability.
Regular maintenance tasks, such as filter changes, component inspections, and seasonal tune-ups, are vital for maintaining efficiency and preventing costly breakdowns.
Building owners and facility managers should stay informed about the latest advancements in HVAC technology, such as smart systems and IoT integration, to leverage their benefits.
Implementing energy-efficient practices and investing in sustainable solutions can lead to significant cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and improved occupant comfort.
As we move towards a more sustainable future, the role of HVAC systems in commercial buildings will continue to evolve.
Embracing new technologies, adhering to stringent regulations, and prioritizing energy efficiency are essential steps for building owners and facility managers.
By investing in high-quality HVAC systems and adopting best practices in design, installation, and maintenance, we can ensure that commercial buildings remain comfortable, efficient, and environmentally responsible.
The commitment to proactive HVAC management and sustainability will not only enhance building performance but also contribute to the broader goals of energy conservation and climate change mitigation.
If you need a new HVAC system, contact us.